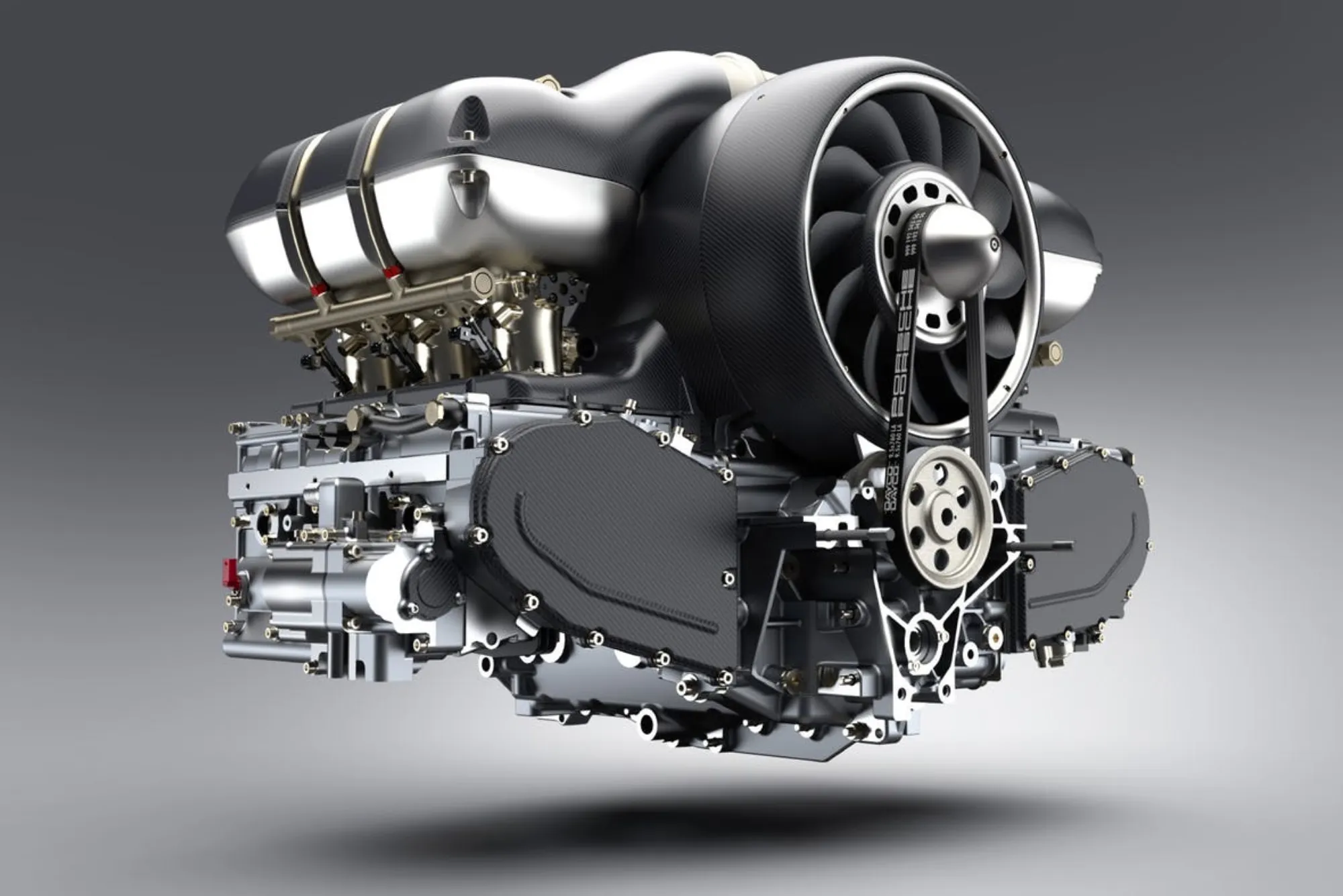
What is an Automobile Engine
An automobile engine is the heart of a vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. Understanding its functionality and components is essential for any car enthusiast or owner.
Types of Automobile Engines
There are various types of automobile engines, including internal combustion engines (ICE), electric motors, and hybrid systems. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications, catering to different vehicle designs and performance requirements.
Components of an Automobile Engine
An automobile engine comprises several key components, including the cylinder block, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and fuel injection system. Each component plays a crucial role in the engine’s operation, contributing to its efficiency and performance.
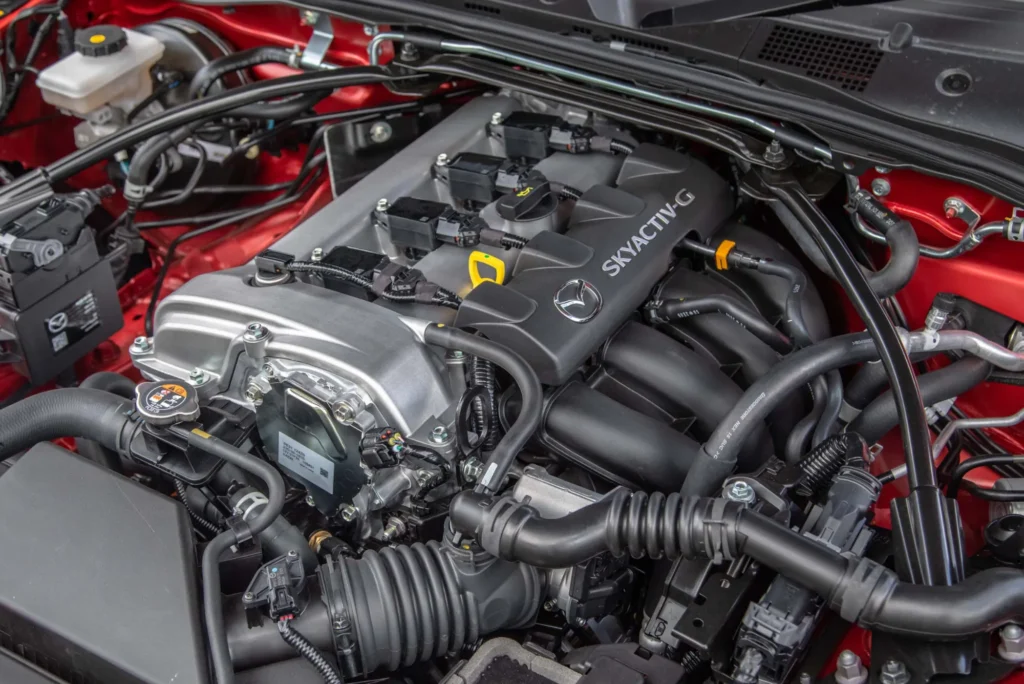

How Automobile Engines Work
In an internal combustion engine, the process begins with air and fuel being mixed in the combustion chamber. The mixture is then compressed by the piston before being ignited by a spark plug, causing a controlled explosion. This explosion generates power, which drives the piston and crankshaft, ultimately propelling the vehicle.
Maintaining an Automobile Engine
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of an automobile engine. This includes routine oil changes, air filter replacements, spark plug inspections, and periodic tune-ups. Proper maintenance can help prevent breakdowns and costly repairs, ensuring smooth operation and efficiency.
The Future of Automobile Engines
With advancements in technology and growing concerns about environmental sustainability, the automotive industry is witnessing a shift towards electric and hybrid engines. These alternatives offer improved efficiency and reduced emissions, reflecting the industry’s commitment to innovation and eco-friendliness.
In conclusion, automobile engines are the driving force behind vehicles, powering them with the energy needed to operate. Understanding the fundamentals of engine operation and maintenance is essential for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, embracing new technologies and sustainable practices, the future of automobile engines looks promising.

Tata AIG Car Insurance
Tata AIG car insurance offers comprehensive coverage for your vehicle, protecting you against financial losses due to accidents, theft, natural disasters, and third-party liabilities. With customizable plans and competitive premiums, Tata AIG ensures peace of mind on the road.
Dublin Auto Spare Parts
Dublin Auto Spare Parts specializes in providing high-quality spare parts for various vehicle makes and models. From engine components to body parts, their extensive inventory ensures customers find the right parts for their vehicles. With a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction, Dublin Auto Spare Parts is your trusted source for automotive components.